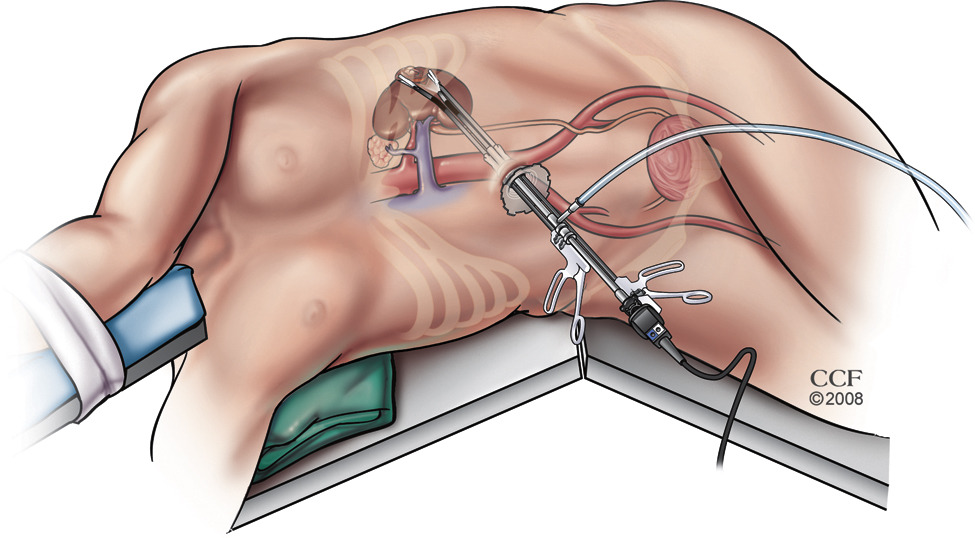
Laproscopic Nephrectomy
A nephrectomy is most commonly used to treat kidney cancer or to remove a noncancerous (benign) tumor. A nephrectomy is sometimes performed to treat a diseased or severely damaged kidney. A donor nephrectomy occurs when a urologic surgeon removes a healthy kidney from a donor for transplant into a person who requires a functioning kidney.
A laparoscopic nephrectomy is an operation that removes one of the two kidneys that are located in the back of the abdomen. An entire kidney is removed during a laparoscopic nephrectomy through keyhole incisions in the flank, the side of the body between the ribs and the hip. The kidney is fully removed (or partly in the case of partial nephrectomy) via an incision that is widened so the organ (or part of it) can be extracted.
Treatment
A nephrectomy is usually done for one of two reasons, either for cancer of the kidney or because of a non-functioning kidney.
- In the case of kidney cancer, radical laparoscopic nephrectomy is done. This is done in an attempt to rid the body of cancer by removing the entire kidney and adrenal gland, with its surrounding fat and attached vessels. In more advanced cases it may be done to stop continued bleeding from the effected kidney.
Symptoms
Kidney cancer usually doesn't have signs or symptoms in its early stages. In time, signs and symptoms may develop, including:
- Blood in your urine
- Pain in your back or side
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Tiredness
- Fever
Tests
The following tests may be recommended by the doctor to confirm the presence of Kidney Cancer:
- Blood and urine testing, CT scans,
- MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging
- Ultrasound
- Renal mass biopsy
2. For non-functioning kidneys, which are either caused by large stones, a lack of blood supply or abnormal kidney structure, a simple laparoscopic nephrectomy is done. A simple nephrectomy is usually done to avoid recurrent infection and pain and the possibility of severe illness because of infection.
Symptoms of acute kidney failure may include:
- Decreased urine output, although occasionally urine output remains normal
- Fluid retention, causing swelling in your legs, ankles or feet
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain or pressure
The following tests may be recommended to verify the presence of acute kidney failure.
- Urine output measurements.
- Urine tests.
- Blood tests.
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- Removing a sample of kidney tissue for testing.
Make an appointment right away for consultation on your urological issue.
Call With Doctor