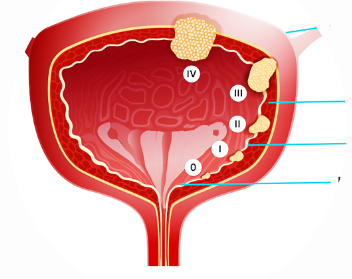
Bladder cancer
Uncontrolled multiplication of Bladder cells leads to bladder cancer. A tumor can emerge when additional cancer cells grow, and over the time that tumor may spread to other areas of the body.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
- Blood in urine(Haematuria)
- Burning or painful sensation while urinating
- Lower back pain on one side of the body
- Frequent urination
- Feeling the need to urinate frequently during the night
- Feeling the need to urinate but not being able to pass urine
Most frequently, bladder cancer is discovered after a patient reports blood in the urine. Gross hematuria is a medical word that denotes the presence of enough blood in the urine for the patient to see it. It's also possible that there are undetectable trace amounts of blood in the urine. This is known as "microscopic hematuria," and a urine test is the only way to diagnose it.
The diagnosis of bladder cancer is made using a variety of diagnostics. Not every test listed here will be applied to every individual.
To identify bladder cancer and learn more about it, the following tests may be used:
- Tests on urine- Urine Routine, Urine for cytology for malignant cells.
- Ultrasound.
- Cystoscopy.
- Bladder biopsy
- Genetic guidance.
- Scan using computed tomography (CT or CAT).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Bone scanning
- PET-CT scans or positron emission tomography (PET).
The principal therapies for bladder cancer generally includes:
- Surgery (LASER TURBT), Laproscopic/ Robotic Radical Cystectomy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted treatment
- local and systemic immunotherapy
- Radiation treatment
Options for treatment and advice are based on a number of variables including the bladder cancer type, grade, stage, and potential side effects, the preferences and general health of the patient
Make an appointment with best Urologist in India Dr Atul Jain for consultation on your urological issue.
Call With Doctor